How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding, adherence to regulations, and a keen awareness of safety protocols. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to confidently navigate the skies, ensuring both safe and successful drone flights.
We’ll explore everything from understanding your drone’s components and pre-flight checks to mastering flight maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll also cover crucial aspects like legal regulations and troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re well-prepared for any situation. Whether you’re a beginner taking your first flight or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide will serve as your trusted companion.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Safe and legal drone operation requires understanding and adhering to regulations and safety procedures. This section covers essential legal requirements, pre-flight checks, and in-flight safety practices to ensure responsible drone use.
Drone Regulations by Location
Drone regulations vary significantly depending on location. Urban areas often have stricter rules regarding flight altitudes and proximity to people and buildings. National parks frequently prohibit drone flights altogether or restrict them to designated areas, often requiring permits. Before flying, always check local and national regulations using resources like the FAA website (for the USA) or equivalent authorities in your country.
Failure to comply can result in fines or legal action.
Drone Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation involves a structured approach encompassing pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight procedures. These procedures mitigate risks and prevent accidents.
- Pre-flight: Check weather conditions, battery levels, propeller integrity, and GPS signal strength. Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- In-flight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone, avoid flying near people or obstacles, and be aware of airspace restrictions. Always keep a backup battery available.
- Post-flight: Safely land the drone, power it off, and store it in a protective case. Review flight logs and footage.
Pre-flight Inspection Checklist
A thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for safe operation. This checklist helps ensure all systems are functioning correctly before takeoff.
- Battery charge level (sufficient for planned flight time)
- Propeller condition (no cracks or damage)
- GPS signal strength (strong and stable)
- Camera functionality (lens clear, settings correct)
- Gimbal operation (smooth and accurate)
- Flight controller status (no error messages)
- Remote controller connection (secure and responsive)
- Weather conditions (suitable for flight)
Drone Safety Features Comparison
Various drones offer different safety features. Understanding these features and their effectiveness is important for selecting a suitable drone and operating it safely.
| Safety Feature | Description | Effectiveness | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Return-to-Home (RTH) | Drone automatically returns to its takeoff point if signal is lost. | High, if GPS signal is strong. | Ineffective in areas with weak GPS signal or interference. |
| Obstacle Avoidance | Sensors detect and avoid obstacles during flight. | Moderate to high, depending on sensor quality and environment. | May not detect all obstacles, especially in complex environments. |
| Low Battery Warning | Alerts the pilot when the battery is low, allowing for a safe landing. | High | Requires pilot awareness and timely response. |
| Geofencing | Restricts the drone’s flight to a predefined area. | High, within the defined area. | Requires proper setup and may not prevent all unauthorized flights. |
Understanding Drone Components and Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the interplay of several key components. Understanding their roles is essential for both operation and troubleshooting.
Basic Drone Components
Most drones share a common set of core components, each playing a vital role in flight and functionality.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires a good grasp of the fundamentals, and a helpful resource for learning is available at how to operate a drone. This guide covers everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, ultimately leading to safe and proficient drone piloting.
- Propellers: Generate thrust for lift and movement.
- Motors: Power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Battery: Provides power to the motors and other onboard electronics.
- Camera: Captures images and videos.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, controlling flight stability and responsiveness. It receives input from various sensors and adjusts motor speeds accordingly.
- GPS Module (in many drones): Provides location data for navigation and features like Return-to-Home.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures the drone’s orientation and acceleration.
- Remote Controller: Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movements.
Component Interrelation
The components work together seamlessly. The flight controller receives data from sensors (like the IMU and GPS), processes this information, and sends signals to the motors to adjust the propellers’ speed and direction, maintaining stability and executing pilot commands. The battery provides the power for this entire process, while the camera records the drone’s perspective.
Drone Types and Specialized Features
Drones come in various sizes and configurations, each designed for specific tasks and applications.
- Racing Drones: Small, lightweight, and highly maneuverable, designed for speed and agility.
- Photography Drones: Larger, often equipped with high-quality cameras and advanced stabilization systems.
- Delivery Drones: Designed to carry and deliver packages.
- Agricultural Drones: Used for crop monitoring and spraying.
Drone Internal Workings Diagram
Imagine a diagram showing the flight controller at the center, receiving input from the IMU, GPS, and remote controller. Arrows indicate the flow of data to the motors, which in turn control the propellers. The battery powers the entire system, and the camera is connected to the flight controller for data and power.
Pre-Flight Preparations and Setup
Proper pre-flight preparation is essential for a safe and successful flight. This involves charging the battery, connecting the controller, calibrating sensors, and planning the flight path.
Charging the Battery and Connecting the Controller
Before each flight, fully charge the drone’s battery using the provided charger. Ensure the battery is properly seated in the drone. Connect the remote controller, making sure it’s properly paired with the drone. Check the controller’s battery level as well.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Calibrating the Drone’s Sensors and Compass
Calibration ensures accurate sensor readings. Most drones have a built-in calibration process that’s initiated through the drone’s app or interface. This typically involves leveling the drone and performing specific movements as instructed by the software. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely.
Flight Path Planning
Plan your flight path carefully, considering wind conditions, obstacles, and airspace restrictions. Avoid flying near power lines, tall buildings, or areas with significant obstacles. Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
Pre-flight Checklist
Use this checklist to ensure everything is ready before takeoff:
- Battery fully charged
- Propellers securely attached
- Controller connected and paired
- Sensors calibrated
- Flight path planned
- Weather conditions checked
- Airspace restrictions verified
- Emergency landing procedures reviewed
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing: How To Operate A Drone
Safe takeoff, flight, and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents. This section Artikels the steps involved.
Safe Takeoff and Landing
For takeoff, gently throttle up until the drone lifts off vertically. Maintain a steady ascent, avoiding sudden movements. For landing, slowly descend until the drone touches down gently. Power off the drone immediately after landing.
Controlling Altitude, Direction, and Speed
Use the control sticks on your remote to adjust altitude, direction, and speed. Practice in an open area to get comfortable with the controls. Avoid abrupt maneuvers, especially at higher altitudes or near obstacles.
Maneuvering in Various Environments

Maneuvering requires adapting to different conditions. In windy conditions, reduce speed and maintain a stable altitude. Around obstacles, use precise control movements to avoid collisions. Always be mindful of your surroundings.
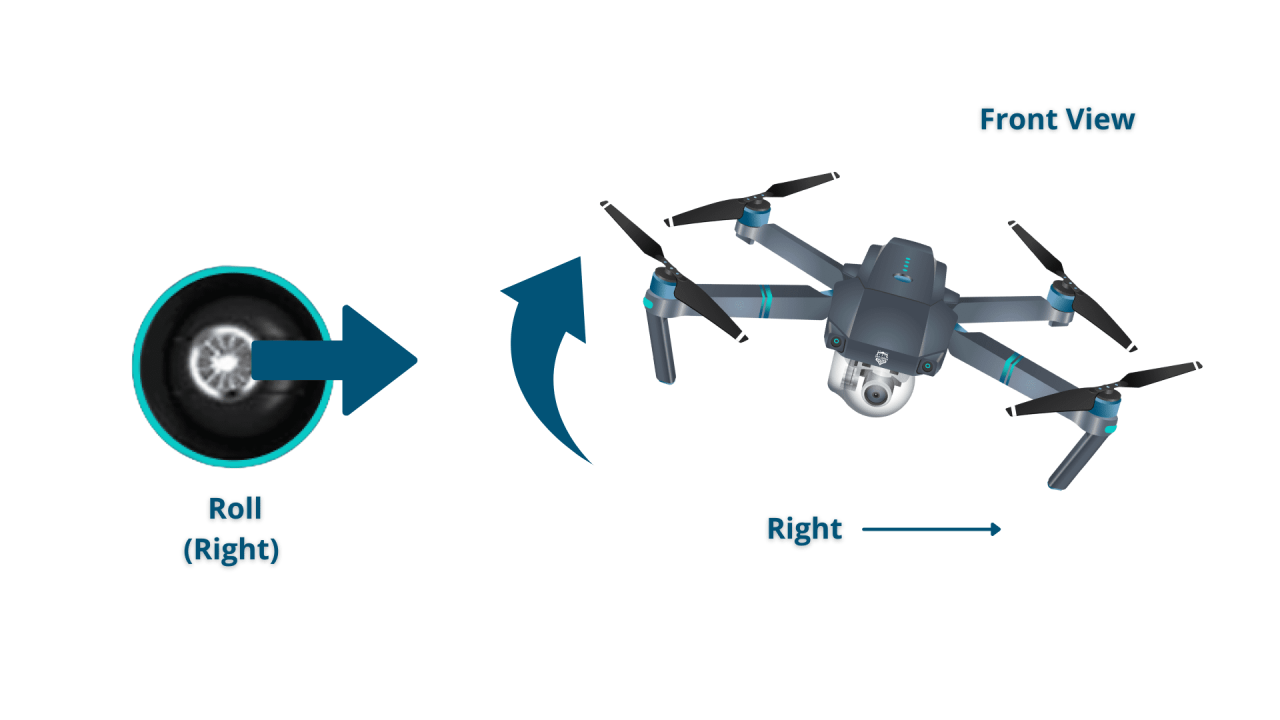
Common Flight Maneuvers
Common maneuvers include hovering, yawing (rotating), pitching (moving forward and backward), and rolling (moving sideways). Practice these maneuvers in a safe environment before attempting more complex movements.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding your drone’s camera settings is essential for capturing high-quality photos and videos. This section details camera features and settings adjustment.
Drone Camera Features and Settings
Most drone cameras offer features like adjustable resolution, shutter speed, aperture, ISO, and white balance. Understanding these settings allows you to tailor image quality to various lighting and shooting conditions.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Resolution determines image size. Shutter speed controls motion blur. Aperture affects depth of field (how much of the image is in focus). ISO impacts image brightness and noise. White balance corrects color temperature.
Capturing Various Types of Shots, How to operate a drone
Experiment with different angles and perspectives. Aerial views offer sweeping landscapes, close-ups provide detail, and time-lapses showcase movement over time.
Camera Modes Summary
| Camera Mode | Description | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Photo | Captures still images. | Landscapes, architecture, close-ups |
| Video | Records moving images. | Time-lapses, aerial footage, events |
| Slow Motion | Records video at a higher frame rate for slow-motion playback. | Action shots, fluid movements |
| HDR (High Dynamic Range) | Combines multiple exposures to capture a wider range of tones. | Scenes with bright and dark areas |
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding common drone problems and their solutions can save time and frustration. This section addresses frequent issues and their troubleshooting steps.
Common Drone Problems and Troubleshooting
Common problems include low battery, signal loss, and motor malfunctions. Low battery is often solved by charging. Signal loss may be due to interference or distance; try moving closer to the drone or finding a location with less interference. Motor malfunctions may require professional repair.
Handling Unexpected Situations
Unexpected situations can arise, such as unexpected wind gusts or loss of control. Always prioritize safety. If losing control, initiate a safe landing procedure immediately. If a motor fails, attempt a controlled descent.
Drone Maintenance and Lifespan Extension

Regular maintenance extends the drone’s lifespan. Clean the propellers and body after each flight. Store the drone in a dry, safe place. Inspect the drone regularly for any damage.
Drone Photography and Videography Techniques
This section focuses on capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos, discussing composition and creative techniques.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
High-quality aerial media requires understanding lighting, composition, and camera settings. Use the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting. Practice various camera angles and movements.
Principles of Composition for Aerial Photography
Apply basic photography rules like the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry. Consider the overall visual impact of the scene.
Creative Aerial Shots and Techniques
Explore creative shots like panoramic views, close-up details, and dynamic movements. Experiment with different flight paths and camera angles to create unique perspectives.
Editing Drone Footage
Editing enhances the final product. Use video editing software to adjust color, add transitions, and create a compelling narrative.
Advanced Drone Features and Capabilities
Many drones offer advanced features that enhance flight capabilities and safety. This section explores some of these features.
Advanced Features: GPS Navigation, Obstacle Avoidance, and Follow-Me Modes
GPS navigation allows for precise flight planning and autonomous return to home. Obstacle avoidance systems help prevent collisions. Follow-me mode allows the drone to automatically follow a subject.
Different Flight Modes
Different flight modes (Sport, Cine, Tripod) adjust responsiveness and stability for various scenarios. Sport mode offers greater agility, while Cine mode prioritizes smooth movements.
Comparison of Drone Models with Advanced Capabilities
Different drone models offer varying levels of advanced features. Research and compare models to find one that meets your needs and budget.
Comparison Table of Drone Features
| Drone Brand | Obstacle Avoidance | GPS RTH | Follow Me Mode | Max Flight Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | Yes | Yes | Yes | 30 minutes |
| Brand B | Yes | Yes | No | 25 minutes |
| Brand C | No | Yes | Yes | 20 minutes |
Successfully operating a drone involves a harmonious blend of technical proficiency, responsible piloting, and creative vision. By understanding the intricacies of your drone, adhering to safety regulations, and mastering essential flight techniques, you can unlock a world of aerial possibilities. Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a skilled and responsible drone pilot. So, take to the skies, capture breathtaking moments, and explore the endless potential of aerial technology responsibly.
FAQ Explained
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions are ideal for beginners. Research models known for their ease of use and robust safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’re in a new location or have experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” function. Activate this immediately. If unavailable, attempt to regain signal, keeping a visual on the drone’s last known location.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions (wind, payload). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your country’s and local civil aviation authority websites for specific drone regulations in your area. These regulations often cover airspace restrictions and registration requirements.
